Heat Sink

Custom Molybdenum Parts Processing -Molybdenum Screw
Grade: Mo1, MLa, TZM Implementation standard: GB/T3877-83 Specifications: processing according to drawings Applications: (1) Used for manufacturing electric vacuum devices and electric light source parts (2) Suitable for processing ion implantation parts (3) Used as high-temperature heating elements and high-temperature structural parts (4) Used as electrodes for furnaces in the glass and refractory fiber industries, working in 1300℃ glass melt with long service life (5) Used as electrodes in the rare earth industry Molybdenum processing parts characteristics: 1. High melting point and good high temperature resistance The melting point of molybdenum plate reaches 2620℃, which is one of the highest melting points among metals. This makes molybdenum plate have excellent stability and corrosion resistance in high temperature environments, and can withstand applications under extreme high temperature conditions, such as furnaces, spacecraft components and high-temperature molten metal containers. 2. High Density and Excellent Mechanical Properties Molybdenum parts have a high density of 10.2 g/cm³, resulting in excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, high hardness, and good tensile strength. This makes molybdenum parts widely used in electronic components, vacuum equipment, the chemical industry, and aerospace. 3. Excellent Thermal and Electrical Conductivity Molybdenum special-shaped parts have excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, among the best among metals. This makes molybdenum parts play an important role in electronic devices, power generation equipment, thermal instrumentation, and fiber optic communications. 4. High Corrosion Resistance and Stability Molybdenum parts exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and stability in most chemical media, demonstrating excellent chemical stability. This has led to their widespread application in the chemical industry, medical devices, optical instruments, and environmental protection. Thread Turning of Molybdenum Alloy Parts Molybdenum alloys have high strength and hardness, but poor toughness, are brittle, and prone to fracture, resulting in poor machinability. However, due to their high melting point, low density, and low thermal expansion coefficient, they are often used in the manufacture of various high-temperature components in the aerospace and aviation industries. Two molybdenum alloy parts, a molybdenum screw and a molybdenum bolt, are shown in the accompanying figure. The incoming blanks were hot-rolled Ø16mm molybdenum alloy steel bars. During processing, it was discovered that the material had low density and very high surface hardness, likely due to residual hardness from annealing. The hardness within the surface layer remained high, with poor toughness and slow thermal conductivity. Using ordinary high-speed steel or carbide cutting tools was extremely difficult. First, the front and rear cutting edges and tips of the cutting

Exploring the Secrets of Tungsten Sputtering Targets: The Material “Magician” of the Microscopic World
In today’s era of rapid technological development, every breakthrough in materials science brings new revolutions to numerous fields. Tungsten sputtering targets, as a key functional material, while less well-known, quietly drive progress in cutting-edge industries such as semiconductors, electronic displays, and optics. From the outside, a tungsten sputtering target appears to be nothing more than a dense, metallic disk or block, but the technological power it embodies cannot be underestimated. Its story begins at the atomic level. Tungsten atoms, with their unique structure and properties, are chosen to shoulder the heavy responsibility of building the microscopic “world of thin films.” Tungsten stands out among metals with its astonishing melting point of 3410°C. This property makes it incredibly stable in high-temperature environments, providing a solid foundation for the sputtering coating process. When a high-energy particle beam, like a fine hail of bullets, whizzes towards a tungsten sputtering target in a vacuum, the tungsten atoms on the target’s surface are ejected one by one, breaking free from their original lattice constraints and scattering into the surrounding space. Like well-trained paratroopers, these atoms are precisely deposited onto the substrate, layer by layer, gradually building up a tungsten thin film with specific functions. Tungsten sputtering targets play an indispensable role in the precision realm of semiconductor chip manufacturing. As chip manufacturing processes advance toward the nanoscale, circuit wiring becomes increasingly refined, making accurate and stable signal transmission critical. With its low resistivity, excellent electromigration resistance, and a thermal expansion coefficient that complements silicon-based materials, tungsten becomes the “invisible bridge” connecting chip components—the contact plugs and wiring. Every tiny tungsten atom deposited contributes to improved chip performance, driving electronic products towards faster, more powerful, and smarter advancements. The electronic display industry is also a playground for tungsten sputtering targets. Tungsten thin film is present in the layers of coatings behind liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and in the critical coatings that ensure efficient and stable electrodes in organic light-emitting diode displays (OLEDs). Like an unsung hero, it precisely controls the reflection, transmission, and absorption of light by adjusting its thickness and microstructure, allowing us to enjoy a vibrant, clear, and smooth visual feast in front of our screens. Whether it’s the exquisite image quality of a mobile phone screen or the stunning visual experience of a large-screen TV, the silent dedication of tungsten sputtering targets is indispensable. The manufacturing of optical devices is even more inseparable from the magical “magic”

A Domestic Pioneer In High-purity Tungsten Target Technology
Background on the technological breakthrough in high-purity tungsten targets The term “high-purity tungsten sputtering targets” may sound complex and unfamiliar, but they play an indispensable and challenging role in the manufacturing of memory and radio frequency chips. For a long time, this critical material was monopolized by a foreign company. FOTMA specializes in ultra-high-purity metal materials, with high-purity tungsten sputtering targets being one of its core products. The research and development and production of these materials are crucial for advancing the manufacturing processes of memory and radio frequency chips in China. Our company’s first independently developed intelligent mass production line for ultra-high-purity tungsten target blanks has successfully commenced production, marking the achievement of full domestic production in raw material preparation, process development, and mass production line design and assembly. FOTMA Precision Materials has achieved a significant breakthrough in mastering core technologies, successfully breaking its previous dependence on imports. This breakthrough was not achieved overnight, but rather required long-term technical accumulation and unremitting efforts. While tungsten is common in everyday life, producing high-purity tungsten is a highly challenging technology. The company’s research team has dedicated over a decade to the research, development, and application of high-purity refractory metals, ultimately achieving a key technological breakthrough. Key Preparation Technology After countless trials and refinements, FOTMA Precision Materials successfully developed a revolutionary high-purity material preparation technology—high-temperature, high-pressure vapor deposition. This technology enables the deep purification of tungsten, a metal with an extremely high melting point, to purity levels exceeding 8N, currently the highest internationally. In materials science, purity is typically measured in “N,” with higher numbers indicating higher purity. For example, tungsten with a purity of 99.999% is designated as 5N, while 99.999999% is designated as 8N. Achievements in Raw Material Preparation Today, FOTMA has achieved large-scale production of high-purity tungsten targets, with an annual production capacity of 1,000 pieces, fully meeting domestic market demand and breaking the long-standing reliance on imports for high-purity tungsten. This achievement is the product of the FOTMA team’s tireless efforts and accumulated technological expertise. We have also demonstrated exceptional capabilities in transforming leading technologies into practical productivity. We have successfully developed key equipment such as fully enclosed vapor deposition equipment and vacuum distillation. These equipment features a high degree of automation, ensuring stable and efficient material preparation. Business-Government Collaboration Local Support FOTMA Precision Materials’ development in China has also received strong support from local governments. In recent years, the local

What is a titanium rod used for?
I. Overview of titanium rod As the name implies, titanium rod is a rod-shaped material made of titanium or titanium alloy. Titanium, as a rare metal, stands out in many fields with its unique physical and chemical properties. The birth of titanium rod is to make better use of these properties of titanium to meet various industrial and technological needs. II. Discovery and characteristics of titanium The discovery of titanium can be traced back to 1791, when it was first discovered in minerals by British chemist William Gregor. However, it was not until 1940 that Luxembourg scientist William Just successfully extracted pure titanium for the first time. Since then, titanium has gradually entered people’s field of vision and has attracted much attention for its excellent performance. The main characteristics of titanium include: Lightweight and high strength: The density of titanium is only 60% of that of steel, but its strength is comparable to that of steel, or even higher. Corrosion resistance: Titanium shows excellent corrosion resistance in a variety of environments, such as seawater, acid, alkali, etc. High temperature resistance: The melting point of titanium is as high as 1668℃, and it can maintain stable performance at high temperatures. Biocompatibility: Titanium has good compatibility with human tissue and will not cause rejection. 3. Classification of titanium rods According to different components and properties, titanium rods can be divided into pure titanium rods and titanium alloy rods. Pure titanium rods: Made of pure titanium, it has excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility and is often used in chemical, medical and other fields. Titanium alloy rods: Made of titanium alloyed with other metals (such as aluminum, vanadium, molybdenum, etc.), it has higher strength and better mechanical properties and is widely used in aerospace, marine engineering and other fields. Common titanium alloy rods include Ti-6Al-4V (TC4), TA10, etc. 4. Manufacturing process of titanium rods The manufacturing process of titanium rods is complex and delicate, mainly including the following steps: Smelting: Put the titanium raw material into a vacuum melting furnace for smelting, remove impurities, and obtain pure titanium liquid. Forging: Pour the smelted titanium liquid into the mold and form a preliminary rod-shaped structure by forging. Rolling: Roll the forged titanium rod to adjust its size and shape, and improve its density and strength. Drawing: The drawing process further refines the size of the titanium rod and improves its surface finish and precision. V.

What Is Titanium Wire Used For?
As an ordinary person, titanium wire is rarely seen. However, what we usually see is iron wire. Iron wire can be seen everywhere in our lives. Titanium wire is used in industry as commonly as iron wire in life, and many a titanium wire company and titanium wire factory are dedicated to its production and supply. Titanium wire is a silvery-white metal (laboratory) with many excellent properties. The density of titanium is 4.54g/cm³, which is 43% lighter than steel. The mechanical strength is similar to that of steel and twice that of aluminum. Titanium is resistant to high temperatures, with a melting point of 1942K, which is nearly 500K higher than steel. China titanium wire is well-known in the global market for its reliable quality and competitive price. Titanium wire, from subtle medical treatment to vast space, from petrochemicals to daily sports and leisure, all show its unique charm. Especially now with the rise of 3D printing technology. What is particularly striking is that more than 60% of titanium and titanium alloy wires are used as welding wires, like a link connecting the industrial world, carrying the mission of firmness and reliability. For those looking to buy titanium wire for various applications, understanding these properties is key, and many suppliers offer titanium wire for sale to meet diverse needs. Today we mainly talk about the production and manufacturing of titanium wires with reference to φ2.6mm titanium wires. Titanium wire production process: titanium ingot—opening 150—sawing–rolling round bar (φ80mm)—removing black skin (peeling)—rolling φ10mm coil—removing black skin—inspection and grinding—multi-stage wire drawing (11 stretching)—final annealing—finished product (φ2.6mm)—closing. A professional titanium wire factory strictly follows these processes to ensure product quality, while a reliable titanium wire company manages the entire supply chain, including maintaining adequate titanium wire stock for timely delivery. The main process used for titanium wire: wire drawing. Wire drawing (fixed die drawing) refers to a processing method in which the wire passes through the die hole under a certain tensile force, “plastic deformation occurs, the cross section is reduced, and the length is increased”. Under the action of the drawing force, the wire rod or wire blank is slowly pulled out, and after fine carving of the die, it finally becomes a titanium wire with a small cross section. Whether for individual purchases or wholesale titanium wire orders, the quality of the finished product depends heavily on this process. There are two ways of wire drawing (fixed die drawing): hot drawing, which is drawing above the recrystallization temperature. Cold drawing,

Technology Of Cold-Rolling Tc4 Titanium Alloy Titanium Tube
TC4 titanium alloy is one of the most widely used titanium alloys at present. It has high strength and good corrosion resistance, but in the seamless titanium tube market at home and abroad, titanium tube manufacturers (titanium tube manufacturers) and titanium tube suppliers (titanium tube suppliers) rarely provide seamless titanium tubes made of TC4 material. TC4 titanium materials are mainly plates. In the current market, the available TC4 titanium tubes (titanium tube for sale) are mostly high-strength thick-walled tubes produced by hot extrusion or oblique perforation. Due to the complex processing equipment and cumbersome processes, the titanium tube price (titanium tube price) of such products remains relatively high, which limits their application range. For titanium tube factories (titanium tube factory) and companies, this has long been a technical bottleneck in expanding product lines—especially for titanium round tube (titanium round tube) products, which are in high demand in industrial fields. The warm rolling process traditionally used requires improving traditional rollers by installing induction heating devices on tube rolling mills. This processing equipment has a complex structure, cumbersome processes, and high production costs. The main reason for this situation is that TC4 titanium alloy has high strength and is difficult to cold-roll form. To solve the key technology of cold-rolling forming of TC4 seamless tubes, schools and enterprises have jointly conducted a series of researches. For example, using the direct cold-rolling forming process to produce high-strength titanium alloy tubes not only greatly reduces production costs but also provides more choices for downstream customers who want to buy titanium tube (buy titanium tube), including wholesale titanium tube (wholesale titanium tube) and customized orders. In the context of global industrial demand, China titanium tube (china titanium tube) enterprises (titanium tube company) have been actively breaking through technical barriers. This cold-rolling technology breakthrough is particularly significant for titanium tube china (titanium tube china) manufacturers, as it enables the production of custom titanium tube (custom titanium tube) and customized titanium tube (customized titanium tube) products with higher precision and lower costs. It also helps stabilize titanium tube stock (titanium tube stock) supply, ensuring that both standard and special-specification products can meet market needs in a timely manner. The research results show that: In the case of small deformation billet opening, the wall thickness deviation is small and the surface roughness gradually decreases; in the case of large deformation billet opening, the wall thickness deviation is large, which will affect the wall thickness deviation of
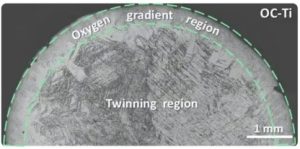
Breaking Through The Performance Limit Of Titanium Alloys, The Intrinsic Fracture Toughness Of Titanium
“What’s exciting is that the fracture toughness of low-oxygen titanium exceeds all commercially pure titanium and titanium alloys reported so far, and even exceeds most metal materials.” Professor Han Weizhong of Xi’an Jiaotong University said. Recently, he and his team successfully broke through the limit performance of titanium and titanium alloys, reducing the oxygen impurity content of commercially pure titanium from 0.14wt.% to 0.02wt.%, and increasing its fracture toughness from 117MPa∙m^1/2 to 255MPa∙m^1/2. Through this study, they also revealed for the first time the ultra-high intrinsic fracture toughness of titanium, breaking the traditional cognition that the fracture toughness of titanium and titanium alloys is less than 130MPa∙m^1/2, proving that low-oxygen titanium is one of the most resilient metal materials known to date. In general, this achievement has brought important inspiration for the design of high-strength and high-toughness titanium alloys. At present, in the field of aerospace, in order to promote the application of titanium alloys under certain safety-critical load conditions, people have adopted the design idea of controlling oxygen content in titanium alloys, which can not only improve the fracture toughness of titanium alloys, but also commercialize related products. For example, damage-tolerant Ti-6Al-4V (TC4 DT) alloy and ultra-low interstitial (ELI) Ti-6Al-4V alloy have been widely used. However, for the current damage-tolerant titanium alloy, the oxygen content in it is still at a high level, resulting in its fracture toughness being limited to below 130MPa∙m1/2. To further improve the application range of classic titanium alloys such as Ti-6Al-4V, it is necessary to improve its service safety. Subsequently, by further reducing the content of oxygen impurities, the fracture toughness of the titanium alloy will be able to achieve a leapfrog improvement. In fact, almost all close-packed hexagonal structure metals, including titanium, zirconium, magnesium, zinc, etc., which are currently widely used, have the phenomenon that <c+a> dislocations are difficult to activate or have poor mobility. This makes their plasticity and fracture toughness far lower than most face-centered cubic structure metals, resulting in limited application range. Therefore, the subsequent alloying design scheme can be used to promote the activation of deformation twins in large quantities. Then, the dense activation of <c+a> dislocations can be promoted through twin boundaries, thereby significantly improving the mechanical properties of close-packed hexagonal metals. It Is Expected To Greatly Improve The Deformation Ability Of Close-Packed Hexagonal Metals Han Weizhong said that he and his team have been paying attention to the influence of dissolved oxygen on the properties of metal

What is molybdenum alloy?
1. Definition and composition of molybdenum alloy Molybdenum alloy, as the name implies, is an alloy material composed of molybdenum as the main component and other elements added. Molybdenum (Mo) is a silvery-white metal element with high melting point, high hardness, and good thermal and electrical conductivity. In molybdenum alloys, the content of molybdenum is usually high, a key factor determining its performance. Beyond molybdenum, the alloy may include elements like iron, nickel, cobalt, chromium, and even copper in specific formulations—such as molybdenum copper or molybdenum copper alloy, which combine molybdenum’s high-temperature resistance with copper’s conductivity. The addition of these elements, including copper in copper moly composites, enhances properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. 2. The proportion of molybdenum in molybdenum alloys applications, molybdenum content ranges widely based on performance needs and use environments. For example, high-strength molybdenum alloys may contain over 90% molybdenum, while alloys requiring high corrosion resistance might adjust molybdenum proportion by adding other elements—including copper in moly copper alloys to balance conductivity and heat dissipation. In copper moly copper structures, the layered composition further tailors properties for specific uses, such as electronic packaging. 3. Properties of molybdenum alloys Molybdenum alloys offer excellent properties from their unique component mix. High molybdenum content grants a high melting point and hardness, ideal for high-temperature environments. Adding elements like copper in molybdenum copper alloy adjusts strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance for diverse applications. For instance, molybdenum copper composites combine molybdenum’s thermal stability with copper’s high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for heat sinks in electronics. Additionally, these alloys maintain good electrical conductivity, critical for applications requiring efficient energy transfer. 4. Preparation process of molybdenum alloys The preparation of molybdenum alloys—including molybdenum copper and copper moly variants—typically involves batching, smelting, pouring, heat treatment, and machining. For molybdenum copper alloy, raw materials like molybdenum powder and copper are accurately weighed, then sintered or infiltrated to form a composite. High-temperature smelting ensures uniform mixing, while heat treatment optimizes the microstructure. Machining converts the alloy into products like moly copper heat spreaders or electrical contacts, with China-based manufacturers often specializing in such precision processes. 5. Application fields of molybdenum alloys Molybdenum alloys, including molybdenum copper and copper moly materials, have wide-ranging uses: Price and market considerations Molybdenum alloy price fluctuates with raw material costs (e.g., molybdenum and copper prices), alloy composition (e.g., high-molybdenum vs. molybdenum copper), and processing complexity. China molybdenum alloy suppliers often offer competitive pricing for standard and custom moly copper or copper moly products, making them preferred choices for industries seeking a balance of performance and cost. Molybdenum alloys—from pure molybdenum-based materials to molybdenum copper alloy composites—deliver versatile performance

What is the difference between 90 10 and 70 30 copper-nickel?
In the field of metal materials, copper-nickel alloys are widely used in many industries due to their unique performance advantages. Copper nickel 70 30 (CuNi70-30) and copper nickel 90 10 (CuNi90-10) are two typical copper-nickel alloys, which have obvious differences in composition, performance, and application. These materials, often supplied by copper nickel manufacturers and copper nickel suppliers, are available in various forms such as copper nickel bar and copper nickel round bar, making them suitable for diverse industrial needs. Chemical composition Physical properties Mechanical properties Corrosion resistance Processing performance Application fields Price considerations When evaluating these alloys, factors like copper nickel 90 10 price, copper nickel price per kg, or copper nickel price per pound vary by supplier, material form (e.g., bar, round bar), and order volume. Manufacturers and suppliers typically provide quotes based on current market rates and product specifications. Copper nickel 70 30 and copper nickel 90 10 each offer distinct advantages in composition, performance, and application. Selecting the right copper nickel material requires balancing use requirements, environmental factors, and cost—with guidance from reliable manufacturers and suppliers to ensure optimal performance. Keywords:copper nickel 90 10 copper nickel bar copper nickel material copper nickel 70 30 copper nickel round bar copper nickel 90 10 price copper nickel manufacturers copper nickel suppliers copper nickel price per kg copper nickel price per pound
INTERESTED IN JOINING OUR TEAM?
Fill out the form below and someone from our team will be in touch with you!
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER
Sign up to see our newest products and exclusive offers!
Hubei Fotma Machinery Co. Ltd.
Wechat / Whatsapp / Mobile:
+86 13995656368, +86 13907199894
Tel: +86-27-67845266
Email: bunny@fotma.com, export@fotma.com
Address: Guanggu Avenue 52#, Hongshan, Wuhan,
Hubei province, P.R.China. 430074