NEWS

What is molybdenum alloy?
1. Definition and composition of molybdenum alloy Molybdenum alloy, as the name implies, is an alloy material composed of molybdenum as the main component and other elements added. Molybdenum (Mo) is a silvery-white metal element with high melting point, high hardness, and good thermal and electrical conductivity. In molybdenum alloys, the content of molybdenum is usually high, a key factor determining its performance. Beyond molybdenum, the alloy may include elements like iron, nickel, cobalt, chromium, and even copper in specific formulations—such as molybdenum copper or molybdenum copper alloy, which combine molybdenum’s high-temperature resistance with copper’s conductivity. The addition of these elements, including copper in copper moly composites, enhances properties like strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. 2. The proportion of molybdenum in molybdenum alloys applications, molybdenum content ranges widely based on performance needs and use environments. For example, high-strength molybdenum alloys may contain over 90% molybdenum, while alloys requiring high corrosion resistance might adjust molybdenum proportion by adding other elements—including copper in moly copper alloys to balance conductivity and heat dissipation. In copper moly copper structures, the layered composition further tailors properties for specific uses, such as electronic packaging. 3. Properties of molybdenum alloys Molybdenum alloys offer excellent properties from their unique component mix. High molybdenum content grants a high melting point and hardness, ideal for high-temperature environments. Adding elements like copper in molybdenum copper alloy adjusts strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance for diverse applications. For instance, molybdenum copper composites combine molybdenum’s thermal stability with copper’s high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for heat sinks in electronics. Additionally, these alloys maintain good electrical conductivity, critical for applications requiring efficient energy transfer. 4. Preparation process of molybdenum alloys The preparation of molybdenum alloys—including molybdenum copper and copper moly variants—typically involves batching, smelting, pouring, heat treatment, and machining. For molybdenum copper alloy, raw materials like molybdenum powder and copper are accurately weighed, then sintered or infiltrated to form a composite. High-temperature smelting ensures uniform mixing, while heat treatment optimizes the microstructure. Machining converts the alloy into products like moly copper heat spreaders or electrical contacts, with China-based manufacturers often specializing in such precision processes. 5. Application fields of molybdenum alloys Molybdenum alloys, including molybdenum copper and copper moly materials, have wide-ranging uses: Price and market considerations Molybdenum alloy price fluctuates with raw material costs (e.g., molybdenum and copper prices), alloy composition (e.g., high-molybdenum vs. molybdenum copper), and processing complexity. China molybdenum alloy suppliers often offer competitive pricing for standard and custom moly copper or copper moly products, making them preferred choices for industries seeking a balance of performance and cost. Molybdenum alloys—from pure molybdenum-based materials to molybdenum copper alloy composites—deliver versatile performance

What is the difference between 90 10 and 70 30 copper-nickel?
In the field of metal materials, copper-nickel alloys are widely used in many industries due to their unique performance advantages. Copper nickel 70 30 (CuNi70-30) and copper nickel 90 10 (CuNi90-10) are two typical copper-nickel alloys, which have obvious differences in composition, performance, and application. These materials, often supplied by copper nickel manufacturers and copper nickel suppliers, are available in various forms such as copper nickel bar and copper nickel round bar, making them suitable for diverse industrial needs. Chemical composition Physical properties Mechanical properties Corrosion resistance Processing performance Application fields Price considerations When evaluating these alloys, factors like copper nickel 90 10 price, copper nickel price per kg, or copper nickel price per pound vary by supplier, material form (e.g., bar, round bar), and order volume. Manufacturers and suppliers typically provide quotes based on current market rates and product specifications. Copper nickel 70 30 and copper nickel 90 10 each offer distinct advantages in composition, performance, and application. Selecting the right copper nickel material requires balancing use requirements, environmental factors, and cost—with guidance from reliable manufacturers and suppliers to ensure optimal performance. Keywords:copper nickel 90 10 copper nickel bar copper nickel material copper nickel 70 30 copper nickel round bar copper nickel 90 10 price copper nickel manufacturers copper nickel suppliers copper nickel price per kg copper nickel price per pound

Introduction To Titanium Plates And Titanium Alloy Plates That Are Not Common In Buildings
Basic knowledge of titanium metal The element titanium (Titanium) was first discovered by British scientist Gregor in ilmenite in 1791. Later, German chemist Klaprus also discovered it from rutile in 1795 and named it “titanium”. However, due to the extremely high chemical activity of titanium, the refining process is quite difficult. It was not until 1910 that American scientist Hunter successfully extracted pure titanium for the first time through sodium reduction. In 1940, Luxembourg scientist Kroll further adopted the magnesium reduction method and successfully produced sponge titanium, thus laying a solid foundation for the large-scale industrial production of titanium. It is worth mentioning that the reserves of titanium in the earth’s crust are considerable. It ranks fourth, second only to iron, aluminum, and magnesium, and its reserves far exceed the sum of commonly used metals copper, nickel, lead, and zinc. In industry, ores such as rutile, white titanium ore, perovskite, and ilmenite are widely used to produce titanium. In addition, titanium metal also has many excellent properties. From the appearance, it is silver-gray, similar to steel, but its performance is better than ordinary metals. ① Titanium metal has low density and high strength, which is very suitable for the needs of lightweight construction. Its density is 4.54g/cm3, which is only 56% of ordinary structural steel, but its strength is equivalent or higher. Among metal structural materials, titanium’s specific strength (that is, the ratio of material strength to density) ranks among the best. In addition, adding a small amount of titanium to the alloy can significantly improve its performance. ② Titanium can react quickly with oxygen in the natural environment to form a strong oxide film, which gives it excellent corrosion resistance. This oxide film can remain stable in oxidizing acids, alkalis, and salt media, especially in wet chlorine and seawater, where its corrosion resistance is even better. Therefore, titanium is very suitable for harsh environments such as seaside, acid rain and volcanic areas. ③ Titanium’s expansion coefficient is about half that of stainless steel and copper, which makes it less stress when the temperature changes. Therefore, it is very suitable for use in environments with large temperature changes, such as the roof of a building. ④Titanium is a non-combustible material with a melting point of up to 1660℃ and can withstand a high temperature of 1100℃ in a fire. In addition, titanium alloys also have excellent thermal strength, which is far superior

Ni200 Nickel Plate: Performance,Application and Processing Technology
Ni200 nickel plate is a high-purity, high-performance metal material. The following is a detailed introduction to it: 1. Composition and structure Main composition: Ni200 nickel plate is mainly composed of nickel elements, with a nickel content of more than 99.6%, and the rest are trace impurity elements such as iron, carbon, silicon, sulfur, phosphorus, etc. Structural characteristics: It has a face-centered cubic lattice structure, which gives it good strength and toughness. 2. Physical and chemical properties Corrosion resistance: Ni200 nickel plate shows good corrosion resistance in a variety of corrosive media, especially in reducing media, its corrosion resistance is particularly outstanding. This makes Ni200 nickel plate widely used in chemical equipment, seawater desalination equipment and other fields. Electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity: Ni200 nickel plate has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity, and its electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity are relatively high. This makes Ni200 nickel plate widely used in electronic components, vacuum devices, precision instruments and other fields. Mechanical properties: Ni200 nickel plate has good mechanical properties, including tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, etc. Although its mechanical properties are relatively low (such as tensile strength of 380 MPa and yield strength of 105 MPa), it still has good processing performance and mechanical properties, and can be used to manufacture parts of various shapes through cold processing and slight processing. 3. Application fields Chemical industry: Ni200 nickel plate is widely used in the chemical industry, mainly used to manufacture corrosion-resistant chemical equipment, pipelines, valves, etc. Its good corrosion resistance can ensure the long-term stable operation of equipment in corrosive media. Electronic field: Ni200 nickel plate also has important applications in the electronics field, mainly used to manufacture electronic components, electric vacuum devices, etc. Its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity can meet the needs of electronic components for high-performance materials. Aerospace field: In the aerospace field, Ni200 nickel plate is used to manufacture high-temperature structural parts, heat shields, etc. Its good high temperature performance and corrosion resistance can ensure the stable operation of equipment in extreme environments. Other fields: Ni200 nickel plate is also widely used in medical, nuclear industry and other fields. For example, in the medical field, Ni200 nickel plate is used to manufacture medical devices such as artificial joints and dental implants; in the nuclear industry, Ni200 nickel plate is used to manufacture protective screens, heat exchangers and other equipment for nuclear reactors. IV. Processing and heat treatment process Casting process: Melting: Since Ni200 has a high melting point (about 1453°C),
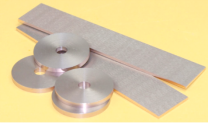
Tungsten-copper Composite Material: An Efficient Electrode Material For Multiple Applications
Application of tungsten-copper composite materials in EDM and welding processing Tungsten, a metal element, is theoretically considered an ideal electrode material. Its excellent strength, density and high hardness characteristics, coupled with a melting point close to 3400°C, make the tungsten electrode extremely low in practical applications. For this reason, tungsten-copper composite materials play a vital role in the field of EDM and welding. However, although pure tungsten has many advantages in theory, it faces two major problems when used as an electrode: one is that it is extremely difficult to process, and the other is that it is relatively expensive. In order to overcome these challenges, scientists have cleverly combined the excellent properties of pure copper, such as plasticity and high conductivity, to develop tungsten-copper composite materials. This material not only retains the high strength, high density and high hardness of tungsten, but also incorporates the processing advantages of copper, making it an ideal electrode choice in the field of EDM and welding. Tungsten-copper composite materials not only have excellent electrical conductivity and high softening temperature, but also have arc corrosion resistance and high wear resistance, which significantly extends their service life and greatly reduces the frequency of electrode correction. In addition, it can effectively save the cost and maintenance of processing tools while improving productivity, making it an ideal advanced welding material. Next, we will explore the wide range of uses of tungsten copper. 1. Advanced EDM electrode materials: During the electro-erosion process, ordinary electrodes tend to have large losses and slow processing speeds for molds such as tungsten steel (hard alloy), high-speed steel, and high-temperature resistant super-hard alloy. However, tungsten copper materials can significantly improve the accuracy of the processed parts due to their excellent electro-erosion speed, low loss rate, precise electrode shape, and excellent processing performance. 2. Advanced welding electrode materials: Combining the dual advantages of tungsten and copper, this type of material is not only resistant to high temperatures and arc ablation, but also has excellent resistance to fusion welding and low cut-off performance. Its high strength, high specific gravity, and excellent electrical and thermal conductivity make it an ideal choice for processes such as spot welding, butt welding, butt welding, and projection welding. In addition, the material is easy to cut and has unique sweat cooling and anti-adhesion properties, making it particularly suitable for applications that require wear resistance and high temperature stability. 3. Application materials in the electronics

Unveiling the Versatile World of Cemented Carbide Products: Powering Industries Across the Globe
In the realm of advanced materials, few substances match the durability, precision, and adaptability of cemented carbide products. These engineered marvels, composed of tungsten carbide particles bonded with cobalt or nickel, have become the backbone of industries demanding extreme strength and resilience. From the cutting-edge floors of a cemented carbide factory to the global supply chains of cemented carbide suppliers, the influence of these materials spans far beyond their unassuming appearance. Let’s delve into the diverse applications that make cemented carbide an indispensable asset in modern manufacturing. 1. Industrial Machining: The Cutting Edge of Precision In the world of metalworking, cemented carbide products reign supreme as the go-to material for cutting tools. Their extraordinary hardness (second only to diamonds) and resistance to heat and wear make them ideal for milling, turning, and drilling even the toughest alloys. Whether shaping aircraft components or machining automotive parts, carbide tools outperform traditional steel by up to 10 times in longevity, reducing downtime and boosting productivity. Cemented carbide manufacturers invest heavily in research to refine tool geometries, such as coated carbide inserts that minimize friction and enhance surface finish. For instance, a cemented carbide company specializing in aerospace applications might develop custom tools for machining titanium alloys, a process where carbide’s thermal stability is non-negotiable. In China, a hub for carbide production, innovative cemented carbide China enterprises have elevated tool design to meet global standards, supplying precision tools to automotive giants and electronics manufacturers. 2. Oil & Gas: Withstanding Harsh Subterranean Environments The oil and gas industry thrives in some of the most unforgiving environments on earth, and cemented carbide products are vital to its operations. Drill bits and downhole tools faced with high-pressure, high-temperature conditions rely on carbide’s abrasion resistance to penetrate rock formations. A single carbide-tipped drill bit can withstand thousands of rotations in granite-like strata, far outperforming conventional steel bits. Cemented carbide factories equipped with advanced sintering technology produce specialized components like valve seats and wear rings for oilfield equipment. These parts endure constant erosion from abrasive fluids, ensuring the longevity of pumps and pipelines. Meanwhile, cemented carbide suppliers coordinate with energy companies to deliver custom solutions, from carbide-coated drill collars to mining tools that withstand corrosive saltwater and acidic gases. In China, where the industry has seen rapid growth, cemented carbide China suppliers have become key players in global energy infrastructure. 3. Aerospace & Defense: Engineering for Extreme Conditions Aerospace applications demand materials that can endure supersonic speeds, extreme temperatures, and high-stress environments—and cemented carbide products rise to the challenge.

What is tungsten copper used for?
Tungsten-copper alloy, with its unique composition and properties, plays a key role in many fields. It combines many advantages of tungsten and copper, such as high temperature resistance, arc erosion resistance, high strength, good electrical and thermal conductivity, and easy cutting. For this reason, this alloy has been widely used in many industrial fields such as machinery, electricity, electronics, metallurgy, and aerospace in different shapes such as tungsten-copper rods, tungsten-copper sheets, and tungsten-copper bars. Specifically, tungsten-copper alloy has shown significant application value in the following aspects: Arc contacts and vacuum contacts of high and medium voltage switches or circuit breakers: Its excellent high temperature resistance and arc erosion resistance make this alloy an ideal choice for making arc contacts and vacuum contacts. Electrodes for EDM: The high strength, high conductivity and good processing performance of tungsten-copper alloy make it occupy a place in EDM. High temperature resistant materials: Its unique physical properties, such as high thermal stability, enable tungsten-copper alloy to maintain its original performance in high temperature environments. Heat dissipation devices on electronic devices: Its good thermal conductivity ensures that electronic devices can effectively dissipate heat during operation. Electrodes for resistance welding: High conductivity and high strength make tungsten copper alloy an ideal choice for resistance welding. Electronic packaging and heat sink materials: In high-power devices such as microwaves, lasers, radio frequency, and optical communications, the high strength and good thermal conductivity of tungsten copper alloys are fully utilized. High-performance lead frames: Its high conductivity and high strength make tungsten copper alloy an ideal material for making high-performance lead frames. Thermal control plates and heat sinks for military and civilian thermal control devices: In the aerospace field, the unique properties of tungsten copper alloys have also been fully utilized. In addition, the chemical composition and physical and mechanical properties of tungsten copper composite materials also provide strong support for its application in various fields. Whether as an electrode for EDM or as an aerospace component, tungsten copper alloy has demonstrated its excellent performance and application potential. Hardness range of tungsten copper alloy Tungsten copper alloy, a unique material that combines tungsten and copper, not only plays a key role in many fields, but its hardness has also become an important performance indicator. Under proper heat treatment and process conditions, the hardness of tungsten copper alloy can be controlled within the range of 50±2.0, which makes it excellent in machining and wear resistance.

Unveiling the Wonders of Titanium Foil: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of advanced materials, titanium foil stands out as a remarkable substance with a plethora of applications and unique properties. From aerospace to medical, and from electronics to jewelry, titanium foil has carved a niche for itself in various industries. This blog post will delve deep into the world of titanium foil, exploring its characteristics, applications, and everything you need to know about purchasing it Understanding Titanium Foil Titanium foil is a thin, flat product made from titanium, a lightweight yet incredibly strong metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength – to – weight ratio, and biocompatibility. It can be produced in various thicknesses, widths, and lengths, making it highly versatile for different uses. The manufacturing process involves rolling titanium ingots into thin sheets, resulting in what we commonly refer to as titanium foil sheet. Titanium foil roll is another common form in which this material is available. These rolls are convenient for industries that require continuous lengths of titanium foil, such as in the production of certain electronic components or for wrapping applications. The flexibility of titanium foil allows it to be easily wound into rolls without causing any damage to its structural integrity. Key Properties of Titanium Foil One of the most outstanding properties of titanium foil is its corrosion resistance. Titanium naturally forms a thin, protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to air, which acts as a barrier against various corrosive substances, including saltwater, acids, and alkalis. This makes it an ideal choice for applications in marine environments, chemical processing plants, and other industries where corrosion is a major concern. In addition to its corrosion resistance, titanium foil has a high strength – to – weight ratio. It is as strong as some steels but much lighter, which is extremely beneficial in aerospace applications where reducing weight is crucial for fuel efficiency. Its biocompatibility is also a significant advantage, especially in the medical field. Titanium is non – toxic and does not cause adverse reactions in the human body, making it suitable for use in medical implants such as dental implants, bone plates, and artificial joints. Applications of Titanium Foil Aerospace Industry In the aerospace sector, titanium foil plays a vital role. It is used in aircraft structures, including fuselage skins, wing components, and engine parts. Its low weight and high strength help in reducing the overall weight of the aircraft, leading to improved fuel efficiency and performance. The

China’s Titanium Industry Breaks Through To High-end Development
Titanium metal is a key material for aerospace, marine engineering, medical and 3C industries, and plays an irreplaceable role in national economic construction, national defense science and technology industry, people’s livelihood security and other fields. “At present, my country has become a major titanium producer and consumer. In terms of the comprehensive competitiveness of the titanium industry, it is in a leading position in the world, but in terms of high-quality development, it is urgent to make up for shortcomings and accelerate the construction of a new pattern and new advantages of high-quality development.” Recently, Ge Honglin, Secretary of the Party Committee and Chairman of the China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association, said at the 2025 Titanium Zirconium Hafnium Vanadium Branch Annual Meeting and Titanium Valley Industry Development Conference. 1. Output continues to grow and the development trend is stable In 2024, my country’s titanium industry will maintain an overall stable development trend, and the output of titanium products will continue to grow. “In 2024, my country’s titanium industry will maintain an overall stable development trend, the output of titanium products will continue to grow, the titanium industry will show centralized development, titanium consumption will show industry differentiation, and import and export trade will continue to grow.” Ge Honglin pointed out. Ge Honglin introduced that from January to February this year, my country’s titanium industry maintained a stable and progressive production trend. The output of titanium concentrate was 1.887 million tons, the import volume was 879,000 tons, and the consumption volume was 2.165 million tons, up 3.6%, 26.2%, and 4.5% year-on-year respectively; the output of titanium sponge was 41,000 tons, the export volume was 1,000 tons, and the consumption volume was 40,900 tons, up 12.8%, 28.6%, and 11.7% year-on-year respectively. II. Break through technical barriers and accelerate the pace of localization In recent years, under the guidance of the concept of safety, autonomy and controllability, the non-ferrous metals industry has significantly accelerated the pace of localization, intelligence and large-scale development of large-scale equipment. At present, in the new round of strategic opportunities such as scientific and technological revolution, industrial transformation, and expanding domestic demand, it is necessary to use innovation to gather the momentum of development, openness to gather the power of cooperation, integration to relieve the difficulties of coordination, and mutual benefit to seek shared benefits, so as to promote cross-regional coordination and cross-field integration of the titanium industry, expand the application
INTERESTED IN JOINING OUR TEAM?
Fill out the form below and someone from our team will be in touch with you!
JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER
Sign up to see our newest products and exclusive offers!
Hubei Fotma Machinery Co. Ltd.
Wechat / Whatsapp / Mobile:
+86 13995656368, +86 13907199894
Tel: +86-27-67845266
Email: bunny@fotma.com, export@fotma.com
Address: Guanggu Avenue 52#, Hongshan, Wuhan,
Hubei province, P.R.China. 430074